Uptrends' Multi-Step API monitoring allows you to execute multiple sequential HTTP requests on your API, where incoming data gets parsed, saved to variables, or checked for the presence of specific content. In certain cases, however, the incoming data will need its values transformed or mapped, to make sense of it more easily. Examples include the XML and JSON encoding and decoding functions described in our custom integrations message formatting guide. In addition to these predetermined functions, Uptrends allows you to set User-defined functions. These functions can be used to convert variable values (acquired in a previous step, or from a system variable provided by Uptrends) to a new value.
Available types of user-defined functions
We offer the following types of user-defined functions:
- Regular Expression: this function type allows you to apply a regular expression (RegEx) to your previously created variables. This is useful for extracting specific sections of the response data (such as extracting an authentication code from a Location redirect-header).
- Mapping: the mapping function type allows you to automatically replace certain values in the response with specific other values. For example, if one endpoint uses the terms error or ok (such as Uptrends' own API) while the next one you’ll be interacting with expects the terms incident or healthy, you can use a mapping function to automatically adjust these values to the correct equivalents.
- Hash: Hashing functions are one-way algorithms, taking a message of any length, and transforming it into a fixed-length value. Any given input must always return the same result, making hashing functions useful in securely comparing sensitive data such as passwords, authorization tokens, or digital signatures, without needing to actually exchange them. You can read more about how to use hashing functions in Multi-step API monitors in our article on hashing and encoding.
Creating User-defined functions
You can set up a user-defined function in either the Steps tab of your Multi-Step API monitors, or in the Customizations tab of your (custom) integrations.
-
In the Steps tab of one of your Multi-Step API monitors or the Customizations tab of your (custom) integrations, you can find the User defined functions header near the bottom of the page.
-
Click the Add function button to start defining a new function.
-
Select the appropriate function type: Mapping, Regular expression, or Hash, and give the function an appropriate name - we recommend something simple and without spaces, as you’ll need to refer to it later on.
-
Fill in any additional required information:
- In case of a mapping function, add the individual mappings you require. The mapping function will translate the “From” values to the corresponding “To” values.
- For a regular expression function, specify the RegEx as required. The Regex is matched against the input text, and can be used to extract a specific part of that input.
- For a hashing function that uses one of the HMAC algorithms, fill in the secret key value.
You can add additional functions by repeating these steps, if necessary.
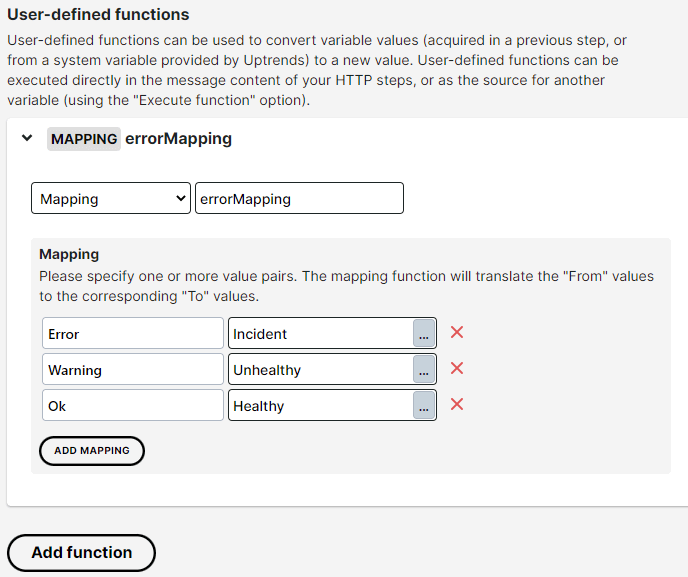
Using your functions
To use your newly defined User-defined function(s), you’ll have to wrap the variable(s) on which the function should act in the function reference like {{userDefinedFunction({{variableReference}})}}. As an example, let’s look at a mapping function whose purpose is to translate incoming response data from ‘Error’ to ‘Incident’, from ‘Warning’ to ‘Unhealthy, and from ‘Ok’ to ‘Healthy’, so that the endpoint called in the following step gets sent the terms it understands. In this example:
- A user-defined function as shown in the image above was created, called
errorMapping. - The endpoint sends a JSON response containing a field ‘Status’, which has a value of either ‘Error’, ‘Warning’, or ‘Ok’.
- In the following step, we intend to forward that status data to a different API. This new API doesn’t understand the terms used, however, and requires values of ‘Incident’, ‘Unhealthy’ or ‘Healthy’ instead.
To use the errorMapping function to automatically translate the status value into the correct terms, follow these steps:
- Extract the value of the ‘Status’ field from the response data, as you normally would (see our Multi-Step monitoring variables set-up guide). In this example, the resulting variable is named statusRaw. As described, this variable will contain ‘Error’/‘Warning’/‘Ok’.
- To apply the user-defined function, first click the Add variable button.
- Set the variable source (the drop-down list on the left) to
Execute function. - For the function expression, wrap the variable reference in the function as described above:
{{errorMapping({{statusRaw}})}} - The resulting value will be either ‘Incident’, ‘Unhealthy’, or ‘Healthy’, depending on what the value of the statusRaw variable was. In the Variable name textfield, specify a name for the output value.
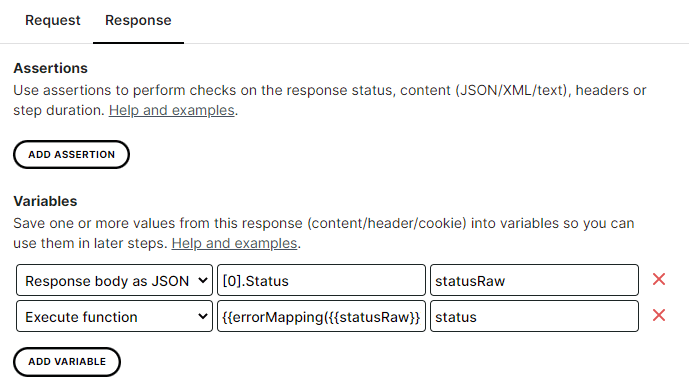
Now we’ve created a new variable, status, whose value is either ‘Incident’ , ‘Unhealthy’, or ‘Healthy’. In following steps, we can refer to this variable in the regular way, e.g. using the {{status}} notation. In this example, we’ve used a Mapping function, but it should be noted that the steps for a RegEx function are identical.